Table of Contents
- Introduction: Securing Networks in the Modern Era
- Understanding Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
- Unpacking Virtual Private Networks (VPN)
- Key Differences Between ZTNA and VPN
- Advantages of Implementing ZTNA
- Benefits of Traditional VPNs
- Future of Network Security
Introduction: Securing Networks in the Modern Era
In a world increasingly reliant on digital technologies, safeguarding network access has become a pressing priority for organizations aiming to defend against many cyber threats. Cutting-edge innovations like VPN and ZTNA are used to provide secure remote access, forming robust defenses against potential incursions. Understanding and deploying effective cybersecurity solutions is vital as companies advance towards digital-first business models.
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and the normalization of remote work environments have intensified the imperative for dynamic and stringent security measures. Choosing between Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) and Virtual Private Networks (VPN) is critical as each offers distinct advantages that can reshape an organization’s security stance and operational efficiency.
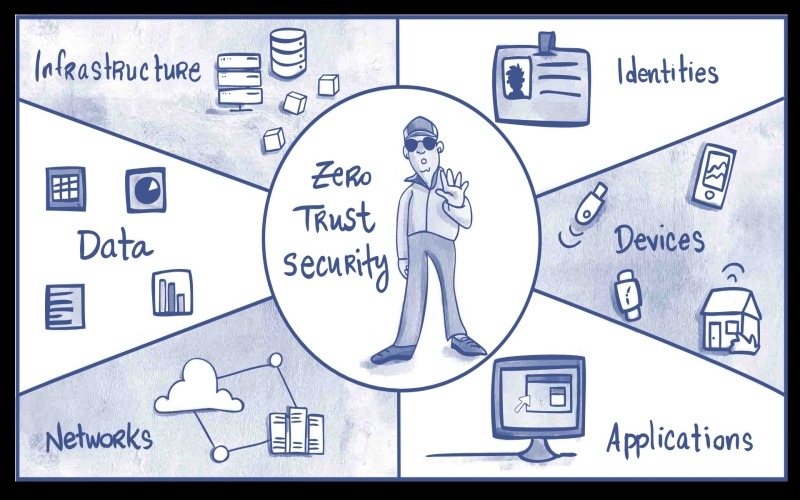
Understanding Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
Zero Trust Network Access, or ZTNA, is a cybersecurity strategy built on “never trust, always verify.” This model aims to mitigate risk by rigorously limiting access to only those users who can be explicitly authenticated, even when operating inside the traditional network perimeters. Unlike conventional security frameworks that grant implicit trust post access, ZTNA continuously monitors and verifies users, ensuring only sanctioned interactions occur within the network infrastructure.
The strategic adoption of ZTNA is particularly beneficial in environments requiring heightened security for remote teams. Due to the model’s stringent standards, businesses embracing ZTNA often observe enhanced security postures and improved operational efficiency. The rise in ZTNA adoption directly responds to its effectiveness in safeguarding a distributed workforce, as articulated in reports highlighting its role in bolstering enterprise security strategies.
Unpacking Virtual Private Networks (VPN)
Widely regarded as a cornerstone in secure digital communications, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) offer a means to safeguard data by creating encrypted connections over public networks. This process allows remote users to operate as if they were directly connected to a private network, facilitating secure data transmission and maintaining data privacy and integrity against potential interception.
VPNs are critical in securing digital communications within organizations, particularly for those with a dispersed workforce. VPNs maintain their relevance and efficacy despite the advent of newer security technologies, reflecting their enduring value in defending corporate data against evolving cyber threats.
Key Differences Between ZTNA and VPN
The core difference between ZTNA and VPN resides in their distinct approaches to security and user accessibility. VPNs focus on creating securely encrypted connections, allowing users a predefined level of trust once access is granted. This trust continues unless security protocols are breached, offering robust security but with potential vulnerabilities in managing access.
ZTNA, on the other hand, employs a more detailed and refined mechanism that demands continual authentication and verification for every user engagement. This minimizes risk by strictly controlling each access point, ensuring that permissions are layered and monitored consistently. ZTNA’s capacity to adaptively manage access based on user roles and conditions positions it as a more scalable solution for environments that require rigorous oversight.
Advantages of Implementing ZTNA
Adopting ZTNA frameworks offers an array of benefits, primarily centered around heightened security measures through relentless verification processes, which consequently reduce the risk of unauthorized access. By enforcing strict access controls, ZTNA minimizes the possibility of exploitation by ensuring that only authenticated individuals can interact with sensitive resources.
ZTNA’s flexible architecture also integrates with cloud-based applications, optimizing user experiences and engagement in remote contexts. Strategic implementations of ZTNA have been shown to significantly enhance security outcomes, particularly within remote working environments. This adaptation underscores the technology’s potential to reformulate security operations.
Benefits of Traditional VPNs
Even in the face of emerging technology landscapes, VPNs remain a critical element in cybersecurity frameworks across the globe. They provide significant benefits, especially where the primary need is for consistent connectivity across various platforms and devices. VPNs afford broad device compatibility without necessitating profound changes to existing infrastructures or comprehensive employee retraining exercises.
The principal advantage of using a VPN lies in its ability to encrypt communications, ensuring that transmitted data remains secure and confidential. This stability makes VPNs preferred for organizations that maintain secure and reliable communication channels without diving into the complexities of newer security frameworks.
Future of Network Security
As technology advances rapidly, so do network security strategies. Both ZTNA and VPN technologies are poised for continuous evolution to meet the ever-growing demands of cybersecurity. With a heightened reliance on cloud services and remote working, the future may see a hybrid model that incorporates the strengths of both ZTNA and VPN, setting a new standard for secured network access.
This convergence points toward a future where flexible, efficient, and user-friendly network security solutions are vital in combating sophisticated cyber threats. Such forward-thinking strategies will ensure enduring protection and stability in a progressively interconnected digital world.